Intro to the UN, the Charter and International Law

The best MUN delegates will always have a strong general understanding of the UN. This includes:
- Knowing what powers the UN has and what they can do.
- Understanding what solutions work best and how to adapt them for their own committees.
Today, we’ll guide you through everything you need to know about the United Nations and the UN Charter. This guide will set you on the path to becoming an awesome MUN delegate!
United Nations - The Basics
The United Nations provides a platform where countries can discuss and solve pressing international issues.
Through its specialized agencies, programs, and initiatives, the UN works around the world to take on a range of topics, aiming to improve lives and uphold human rights across the globe.
UN history - Creating the UN Charter
The roots of the United Nations trace back to the devastation of World War II, as the war drew to a close, the international community recognized the urgent need to come together and work to prevent catastrophic conflicts from ever happening again.
The first blueprint of the UN was drafted at a conference at Dumbarton Oaks in Washington, D.C. in 1943. Over the next few months, the organization that would eventually become the United Nations came to life.
In April 1945, 50 countries met in San Francisco for the United Nations Conference on International Organization. Over the next few months, these delegates drew up the 111-article, 50 page UN Charter. The Charter was unanimously adopted on 25 June 1945.
The Charter would serve as the 'rule-book' for the the United Nations, providing a framework for international cooperation, conflict resolution, and the protection of human rights.
The United Nations officially came into existence on October 24th 1945, marking a pivotal moment in history - we still celebrate UN day every year on the 24th!
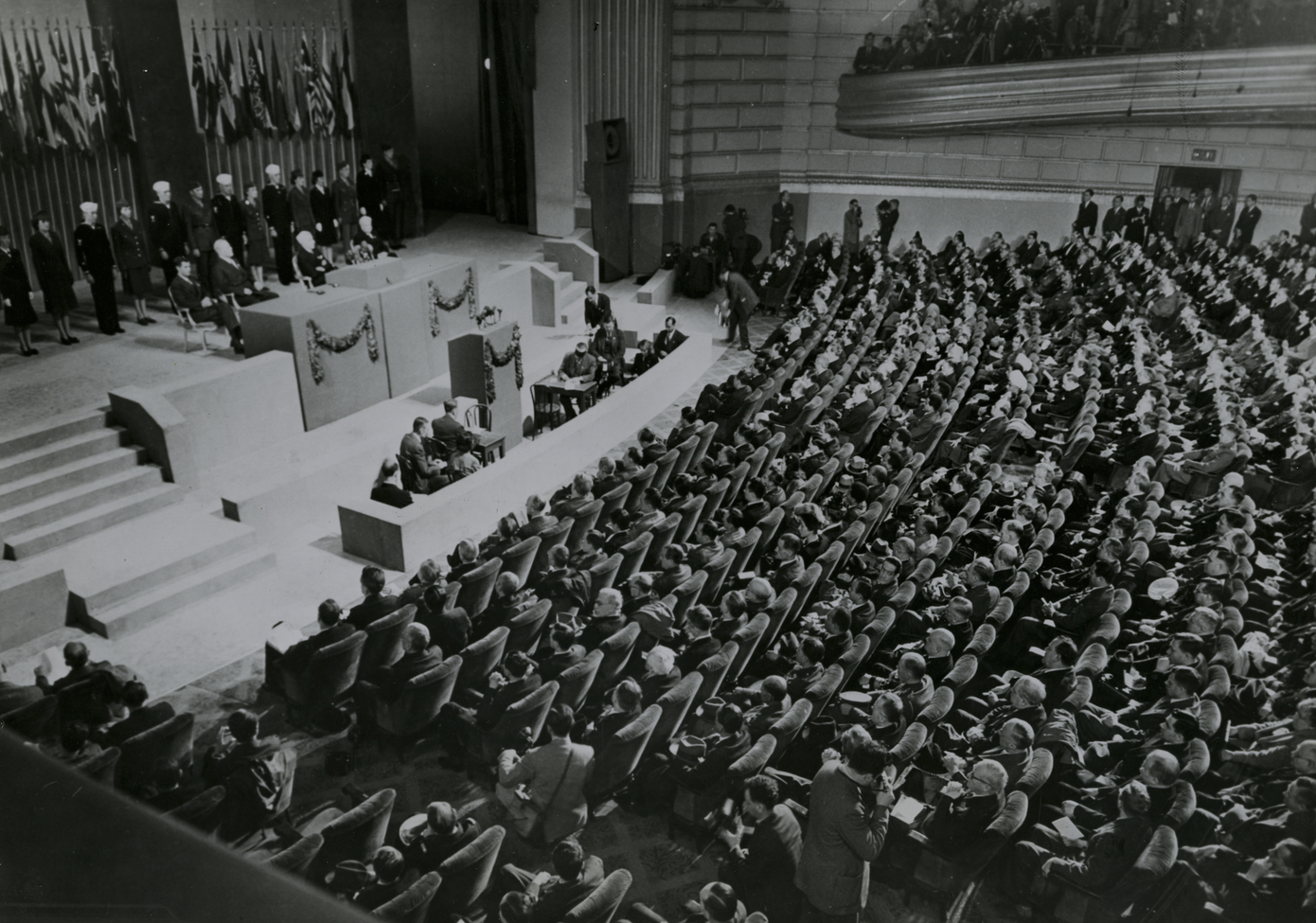

Founding Principles of the United Nations
Since the UN Charter is the rule-book for the United Nations, it includes some of the key principles that the UN should uphold.
While there are many different themes, they all fall under the same two categories:
1- Diplomacy through Dialogue
In a world where tensions can heat up quickly, the Charter provides a framework where countries can address their grievances peacefully. These techniques include: negotiation, mediation, and arbitration.
This approach to diplomacy and dialogue is anchored in a legal and moral compass. Legally, the charter outlines a clear alternative to war by committing them to resolve disputes within the bounds of international law. Morally, nations work to uphold these practices, part of the UN involves committing to certain core principles such as human rights, equality, and justice.
2- Teamwork makes the dream work
The UN Charter adopts the principle of multilateralism - this is a recognition that no single nation can tackle the challenges of the modern world alone.
The best solutions to international problems are those that bring in multiple perspectives and a shared responsibility. Projects like the Sustainable Development Goals are a great example.
Other key principles

The United Nations - Today
UN Membership
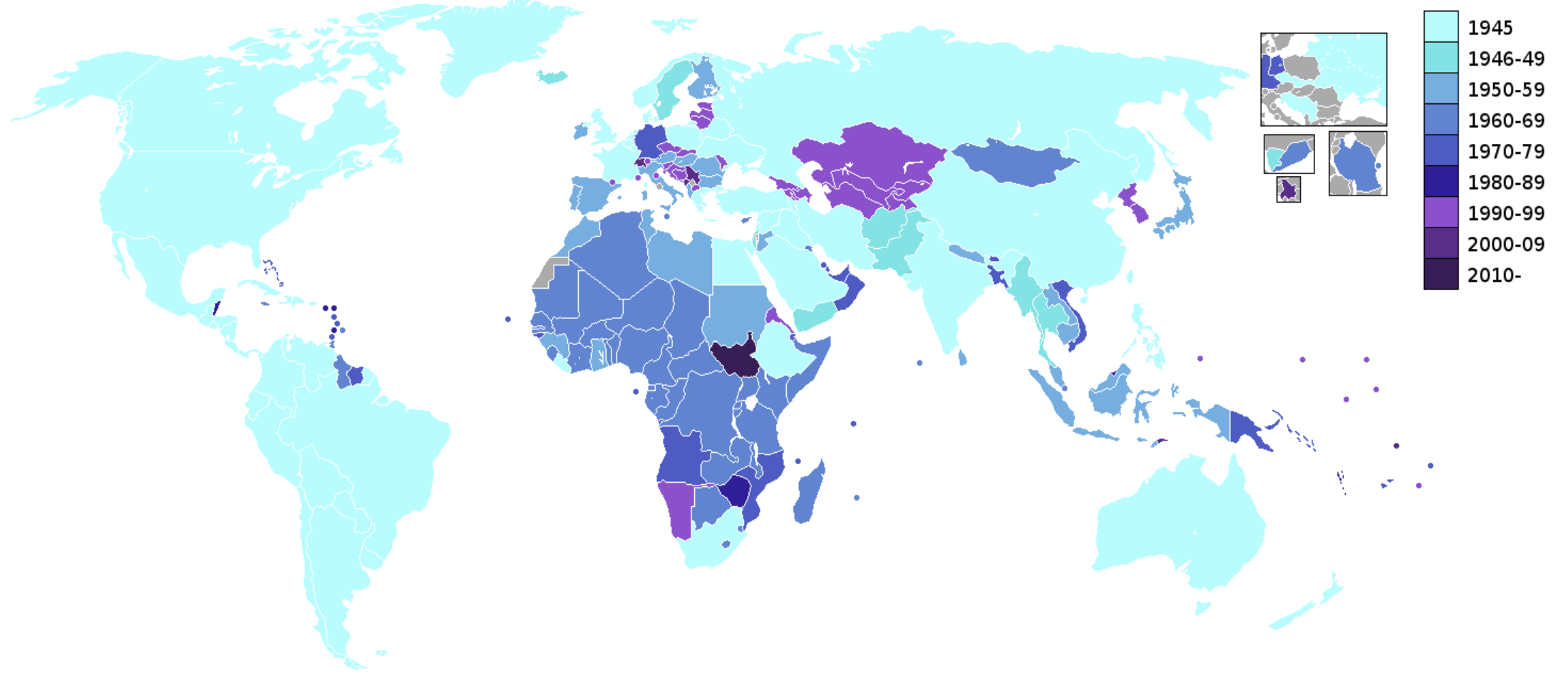
In the decades that followed, the organization experienced significant growth, expanding its membership from the original 50 to nearly 200 member states today.
Membership is open to all countries that agree to uphold the principles outlined in the UN Charter.
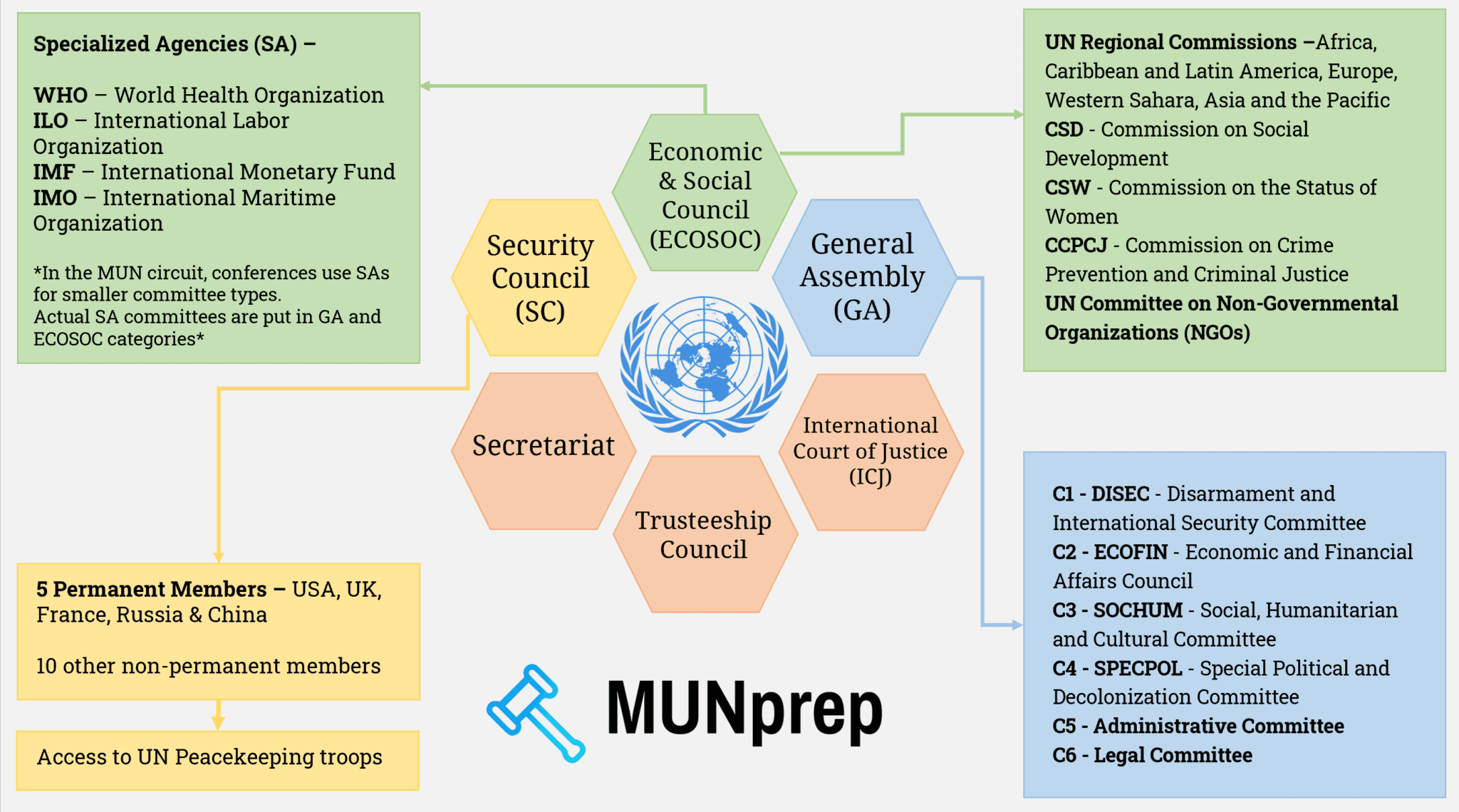
Structure
Nowadays, the UN receives tens of billions of dollars of funding per year and operates in nearly every country around the world. Having so many projects running at the same time requires a lot of organization. To be sure every issue gets the attention it deserves, the UN has developed a system of Organs, Committees, and Offices. This helps them to handle any problem they might face.
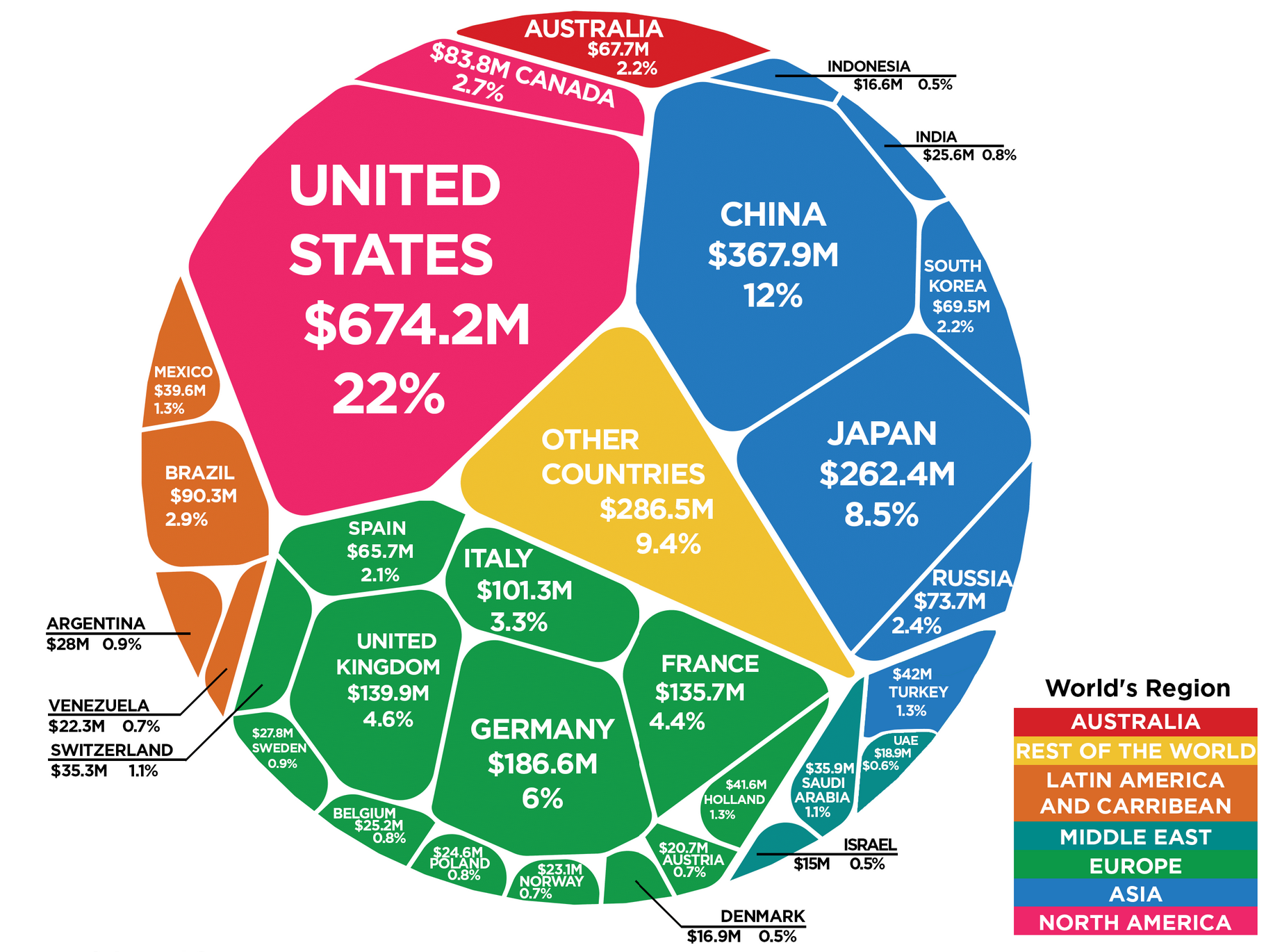
Funding
The UN relies heavily on contributions from its members. With each country required to provide funding based on their economic capacity.
These regular dues, or “assessed contributions” support the UN’s core budget. Projects like UN peacekeeping operations, humanitarian aid, and the maintenance of the UN’s organizational infrastructure rely on these funds.
The United States has historically been the top contributor, normally covering around 22% of the UN's regular budget, China is the second largest contributor with increased contributions in recent years.
Additionally, the UN relies on voluntary funding from governments, private organizations, and individuals. These funds go to specific agencies like UNICEF, the WHO, and the UNDP.
Successes and Failures of the UN
So far, most countries have joined the UN, and the organization has been successful in accomplishing a number of important goals.
We've outlined a few of the biggest UN achievements below.
Significant UN achievements

Many of these accomplishments would never have been possible without an organization like the United Nations bringing people together.
However, the UN is also widely criticized – many say that the organization has not fully lived up to its potential, they blame things like bureaucracy and politics.
UN Challenges
It is true that the UN has not always been successful in achieving its mission. People blame this on a number of different factors, including:
- Inefficiency and bureaucracy: The organization's structure and procedures may hinder its ability to respond swiftly to global challenges.
- Lack of accountability: The UN has faced criticism for instances of misconduct and lack of accountability among its personnel.
- Limited enforcement power: The UN relies heavily on member states' willingness to comply with its decisions and resolutions.
- The veto power: The veto power held by the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) means a single country can overrule a popular vote.
- Threats to State Sovereignty: State sovereignty is the ability of a country to govern itself without foreign interference. Certain UN members have not always upheld this principle.
Balancing the Successes and Failures
While the UN has delivered on enormous projects that we never would have dared to approach without the organization, it is clear that some challenges still remain and the UN has sometimes fallen short of expectations.
From peacekeeping successes to ongoing struggles with reform, the UN’s journey is complex.
By building on past successes and learning from setbacks, we can collectively work toward a more effective and resilient UN, capable of addressing the evolving challenges of our global community.
Next Lesson
Now you everything you need to know about the United Nations, its time to build up your Model UN skills stick with us while we explain the decision-making process in MUN.
See you there!






